Precision is crucial in the dynamic production sector. Today, industries are pushing the limits of design and technology, so innovative fabrication procedures that provide accuracy and dependability are more important than ever.
Then comes micro TIG welding, a revolution in precision engineering. This blog post examines its complexities, uses, benefits, and ways it will influence production in the future.
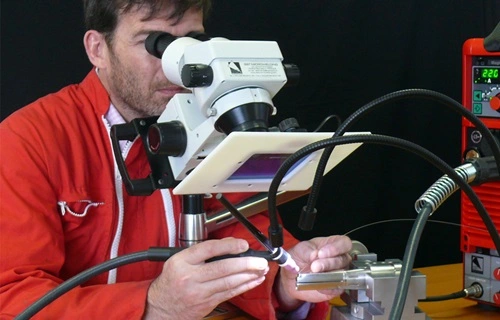
Microscopic TIG welding
This is an arc-welding procedure, also known as pulse arc welding. The technique uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to make an arc that produces the weld.
Like laser welding, microscopic TIG welding is a non-contact method that needs an external fixture to impart force to produce a correct part fit-up. It uses a welding power supply with a steady current to create arcs between the workpiece and the tungsten electrode. The heat produced forms the joint, resulting in high-quality welds with few heat-affected areas.
Micro TIG welding has many benefits. For instance, it eliminates the need for solder and produces a weld that is extremely resilient to heat and vibration.
Which sectors stand to gain from micro TIG welding?
Micro TIG welding is often used to weld tiny areas. These are typically fragile components used in the electronics, automotive, or medical industries.
This kind of welding is frequently used in the medical, military, and space industries, as well as consumer goods like surgical instruments, eyewear, high-performance items, and other markets.
Here are some industries that utilize micro TIG welding:
- Automotive: Used for electronic parts, ignition controls, instrumentation, O2 sensors, potentiometers, solenoids, motor assembly, micro weld cross wire applications, etc.
- Aerospace: Used for exotic metals, thermocouples, mesh welding, honeycomb welding, micro welding, and more.
- Jewelry and Art: Used for porosity, ring size, prong repair, general jewelry repair, fine chain micro welding, and earring posts.
- Research & Development: It is used for electrical connections, ordnance fuses, stranded wire preparation, and wire termination. It is also helpful in welding magnet wire, unique metals, micro-weld inductors, and specialized battery packs.
- Mold and Die: These are used to fix porosity, add material for shimming, repair minor weldments, repair holes, repair EDM pits, and micro-weld mold and die edges.
- Medical devices: Fabricating medical instruments, such as surgical tools and catheters.
- Dentistry: Used for casting porosity, noble metal crowns, micro-weld metal bridges, and other dental appliance malfunctions.
- Optics: A technique for micro welding damaged eyeglass frames.
Keep in mind that microscopic TIG welding requires a high level of expertise. So, using a professional TIG welding company for your production needs is best. This can guarantee the utmost accuracy and reliability.
Micro TIG welding precision benefits
- High precision: It minimizes distortion risk when welding minimal components.
- Versatility: This process is suitable for a variety of materials, including titanium, stainless steel, and some types of plastic.
- Strength and durability: It produces strong welds to endure heavy use.
- The Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) lowers the possibility of heat damage to parts, protecting their structural soundness and operation.
The potential of micro TIG welding in manufacturing
Micro TIG welding’s function is expected to expand as industries continue to develop and demand more significant levels of quality and precision. It will be a crucial technology for precision fabrication in the future. It can produce solid and dependable welds for intricate and delicate components.
Micro Weld serves various industries through microscopic TIG welding. This demonstrates the technique’s adaptability and capacity to satisfy the demands of contemporary manufacturing. Micro TIG welding techniques’ ongoing growth and uptake will surely be crucial in spurring innovation as we go forward. This guarantees that production will be accurate and boundless in the future.
Final thoughts
By adopting technologies such as micro TIG welding, industries are improving their fabrication capacity and establishing new benchmarks for production efficiency, quality, and dependability.

